Environmental Fate of ENMs: Air Compartment
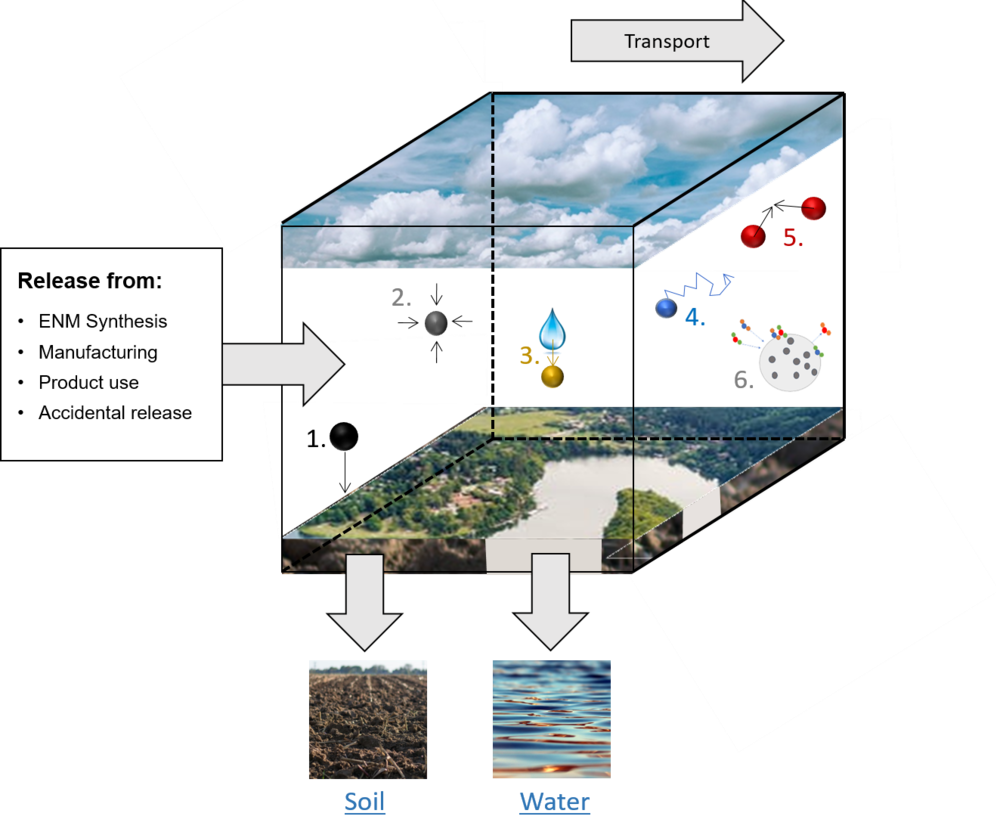
Air is mobile in all three dimensions and can be transported over long distances. A variety of sources can release the emission of pristine ENMs into air. Once emitted, ENMs will be transported and undergo various transformation processes as shown in the figure below. Airborne ENMs will be deposited to the Earth’s surface after a residence time in the air (typically much shorter than residence in water or soil) by either scavenging or dry deposition. Therefore, ENMs do not accumulate in air.
Case studies |
Read also |
|
TiO2 photocatalytic coating for roads |
John AC, Küpper M, Manders-Groot AMM, Debray B, Lacome J-M, Kuhlbusch TAJ (2017) Emissions and Possible Environmental Implication of Engineered Nanomaterials (ENMs) in the Atmosphere. Atmosphere 2017, 8(5), 84; https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8050084 |
Contact
 Carmen Nickel
Carmen Nickel
Institut für Energie- und Umwelttechnik (IUTA)

Christof Asbach
Institut für Energie- und Umwelttechnik (IUTA)
Email: asbach@iuta.de
