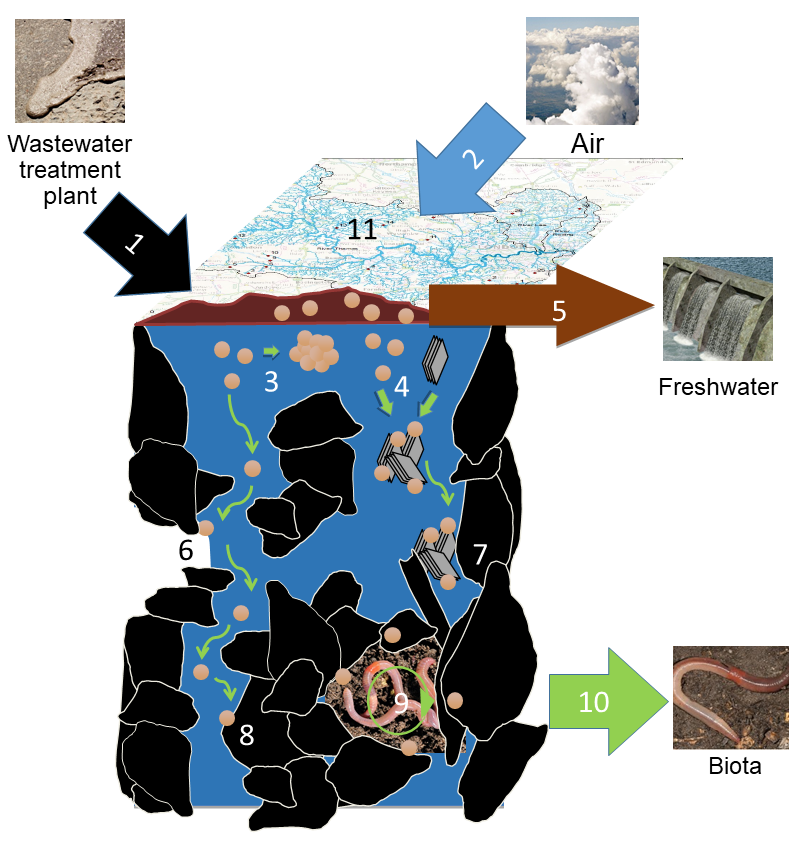
Environmental Fate of ENMs: Soil Compartment
Soils are exposed to ENMs mostly through deposition of sludge on agricultural land. A range of organisms can be exposed and possibly be affected, including food crops, also giving an entry into the human food chains. ENMs are also applied deliberately to soils, e.g. as zerovalent iron to remediate contaminated soils, as nanofertilizers or as nanopesticides.
 |
Case studies |
Read also |
|
Cornelis G, et al. (2014) Fate and Bioavailability of Engineered Nanoparticles in Soils: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 44: 2720–2764. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2013.829767 |
Contact

Geert Cornelis
Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences (SLU)
Email: Geert.cornelis@slu.se
