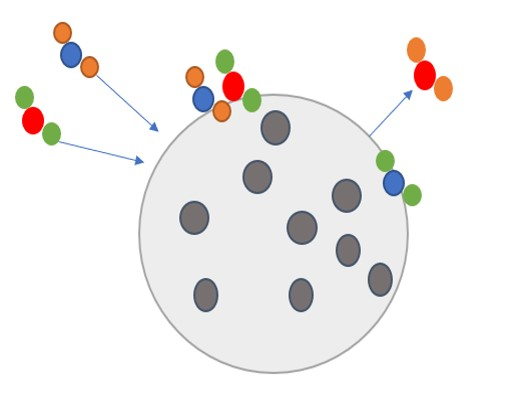
Heterogeneous reaction
Gases can react on an aerosol surface. The reaction rate can be determined using the following parameterization for the reaction constant.
|
|
The reaction rate k is related to
Note that aerosol surface is not equivalent to effective surface (BET), due to presence of pores.
|
Execution |
|
|
These equations are purely deterministic and can easily be solved using a pocket calculator or spreadsheet software. |
Used in |
|
|
|
Read more |
Read also |
|
Consult the NanoFASE Library to see abstracts of these deliverable reports: |
Dentener, F. J., & Crutzen, P. J. (1993), Reaction of N2O5 on tropospheric aerosols: Impact on the global distributions of NOx, O3, and OH. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 98(D4), 7149-7163. |
Contact

Astrid Manders
TNO, Netherlands