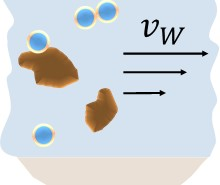
Advective transport
Advective transport describes the movement of some material transported along with the water through a waterway. Examples include the salt dissolved in the oceans, or silt or clay present in a river. In almost all cases the water in a river will not flow steadily but instead rather turbulently. Including the effect of turbulence in the transport of particles is not a straightforward calculation.
 |
Occurs in |
||
|
|
|
 |
|
| Water | Sediment | Soil | |
Fate descriptors |
Algorithms |
||
|
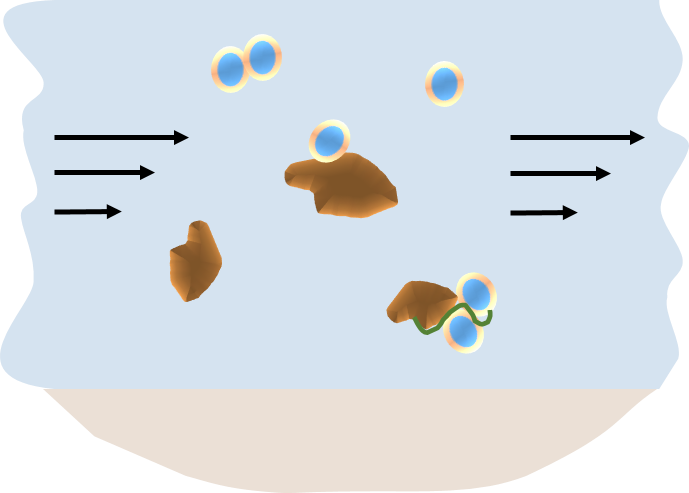
Advective transport in the NanoFASE model
|
Read more |
Read also |
|
Consult the NanoFASE Library to see abstracts of these deliverable reports: |
|
Contact

Frank von der Kammer
University of Vienna, Austria
Email: frank.von.der.kammer@univie.ac.at