Zerovalent iron nanoparticles (nZVI)
Zerovalent iron nanoparticles (nZVI) are used for groundwater remediation. Mobility and remedial performance are enhanced by electric field (DC).
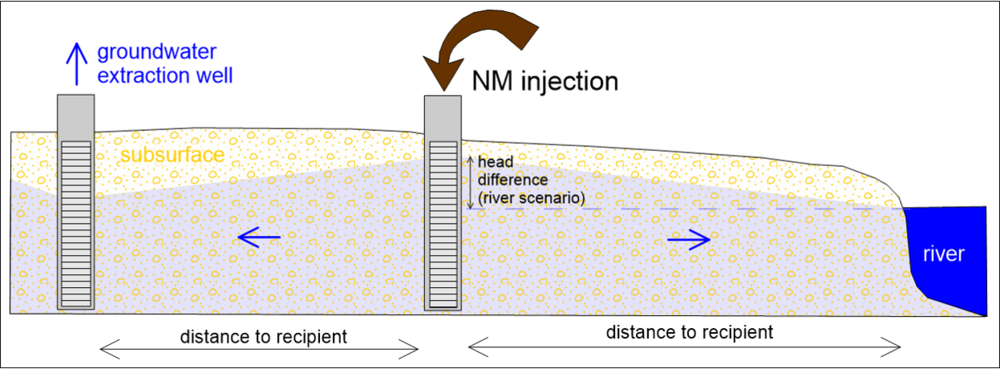
|
The nanoiron model uses migration parameters estimated from easy-to-measure parameters and sand packed column tests. The upscaled model is applied in macrocosm on a contaminated site. Nanoparticles are injected into the borehole where they aggregate, attach and react with both pollutants and electron acceptors in groundwater. At the end of their transformation, the particles oxidize and produce secondary minerals and dissolved iron indistinguishable from naturally occurring iron. |
Occurs in |
Case study |
Read more |
Read also |
|
|
Visit the NanoFASE Library to read summaries: |
Nathanail C.P. et al. 2016. A preliminary risk assessment procedure for renegade nanoparticles deployed during nanoremediation. Remediation Journal. 26(3): 95–108. http://doi.org/10.1002/rem.21471 Also see: http://nanoiron.cz/en/ |
Contact

Jaroslav Nosek
Technical University of Liberec (TUL)
Email: jaroslav.nosek1@tul.cz