Non-saturation correction in the NanoFASE model
The NanoFASE model uses the non-saturation correction factor to take into account empirically the effect of air-water interactions in the transport calculation of nanomaterials in porous media such as soils and sediments. The correction basically modifies the attachment efficiency, making it higher when the degree of saturation is lower.
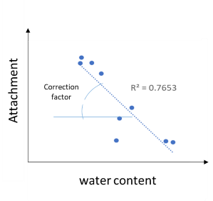 |
\(\alpha _{non-saturated}(\theta )=\alpha _{saturated} +f_{non-saturated}\times 1\) \(\alpha _{non-saturated}\) can then be calculated using the non-saturation correction factor (\(f_{{non-saturated}}\)). |
Execution
Several unsaturated column tests are needed to fit \(f_{air-water}\) to the \(\alpha _{non-saturated}(\theta)\)relation. This relation was found to be linear in NanoFASE, but in a limited set of experiments only. Further research is needed to confirm this relationship. Potentially, the straining factor would depend more clearly on the water content in soil.
|
\(f_{non-saturated}\) |
Used for
|
\(\frac{dC}{dt}=v\theta \frac{dC}{dz}-\) \(D\frac{d^{2}C}{(dz)^{2}}-k_{loss}\) |
|
| Air/water interaction | Transport calculation |
Read more |
Read also |
|
Consult the NanoFASE Library to see abstracts of these deliverable reports: NanoFASE Report D7.2 Soil property - NM fate relationships NanoFASE Report D7.4 Module for NM exposure prediction in soils to couple to overall framework |
OECD technical guideline 312 |
Contact

Geert Cornelis
Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences (SLU)
Email: geert.cornelis@slu.se