NanoFASE Case Study: Uptake and elimination kinetics of Ag-NPs in freshwater snails
During the household or industrial washing of nano-enabled products, silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) can be released to the municipal sewer system, ending up in waste water treatment plants (WWTPs) and transferred to aquatic environments through effluent discharge (Figure 1). Freshwater systems are important sinks for NPs, especially the sediment phase where benthic organisms can be exposed through water and sediment. In this work, we studied the kinetics in freshwater snails of pristine Ag-NPs of different sizes (3-8 nm, 50 nm and 60 nm) and a simulated aged form (Ag2S-NP), produced by NanoFASE partners AMEPOX Enterprise and Applied Nanoparticles. The kinetic parameters derived from this study were included in the NanoFASE model.
Study aim |
Determine uptake and elimination kinetics of different forms of Ag-NPs in the freshwater snail Physa acuta.
Image credit: S. Gonçalves
Experimental approach |
Overview |
|
üAg-NP 3-8, 50, 60 nm
üAg2S-NP 20 nm
üAgNO3
Clean medium
 |
|
Environmental medium: Freshwater NP type/size: Ag-NPs 3-8 nm, 50 nm and 60 nm; Species: Bio-assay: |
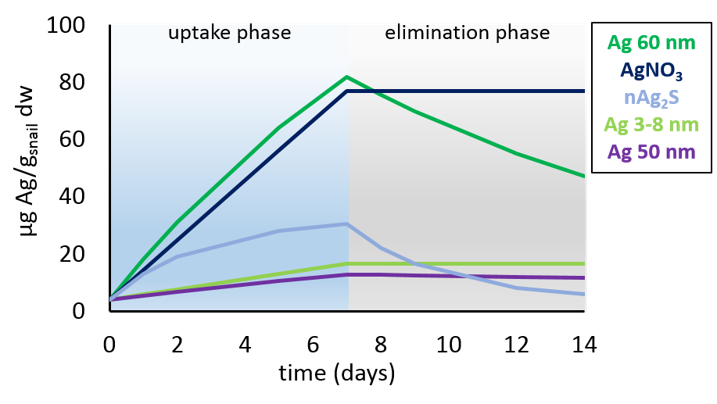
Results |
|
|
|
|
Modelling parameter outputs |
Compartment |
|
|
Read more |
Read also |
|
Visit the NanoFASE Library: Silva PV, van Gestel CAM, Verweij RA, Loureiro S (2019) Toxicokinetics of pristine and aged silver nanoparticles in freshwater benthic organisms: the role of exposure route. SETAC Poster.
|
|
Contact
 Susana Loureiro
Susana Loureiro
Email: sloureiro@ua.pt

Patrícia V. Silva