Dissolution
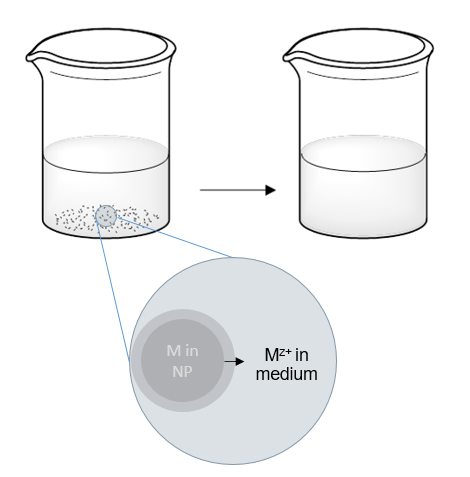
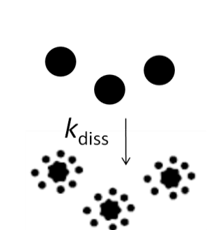
Dissolution is a dynamic process by which ions from a surface of a solid material are released over time into the background solution. Various physicochemical factors affect the dissolution of ENMs. Those include characteristics of particles (e.g. material, surface area, engineered surface coatings, aggregation state) as well as of the exposure media (pH, redox potential, dissolved salts & organics, temperature).
|
|
Occurs in |
Fate descriptors |
Algorithms |
|
|
\(\frac{d[M^{z+}]}{dt} = k_{diss}([M^{z}]_{eq}-[M^{z+}]_{t})\) |
Read more |
Read also |
|
Consult the NanoFASE Library to see abstracts of these deliverable reports: |
Misra et al (2012) – Sci Tot Environ 438, 225-232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.08.066 |
Contact
 Elena Badetti
Elena Badetti
University Ca' Foscari of Venice, Italy
 Julián Gallego
Julián Gallego
University of Gothenburg, Sweden
 Frank von der Kammer
Frank von der Kammer
University of Vienna, Austria
Email: frank.von.der.kammer@univie.ac.at