NanoFASE Case study: AMEPOX AXmc Conductive Ag Ink
NanoFASE partner Amepox Enterprise Ltd. (AXME) is a Polish private SME founded in 1988. Amepox has a production profile with its own R&D laboratory and expertise in the field of multi-function conductive formulations with polymer-based binders. In 2000 Amepox started its activity in the nanotechnology field and developed technology to produce silver (Ag) powders including particles sized close to several atoms in diameter. Subsidiary Amepox Microelectronics (AXmc) produces electronics materials including nanoinks. The release pathway case study assessed in NanoFASE is AXmc's conductive ink containing nano Ag, used to produce flexible printed electronic circuits (for microelectronics, solar cells, and other applications).
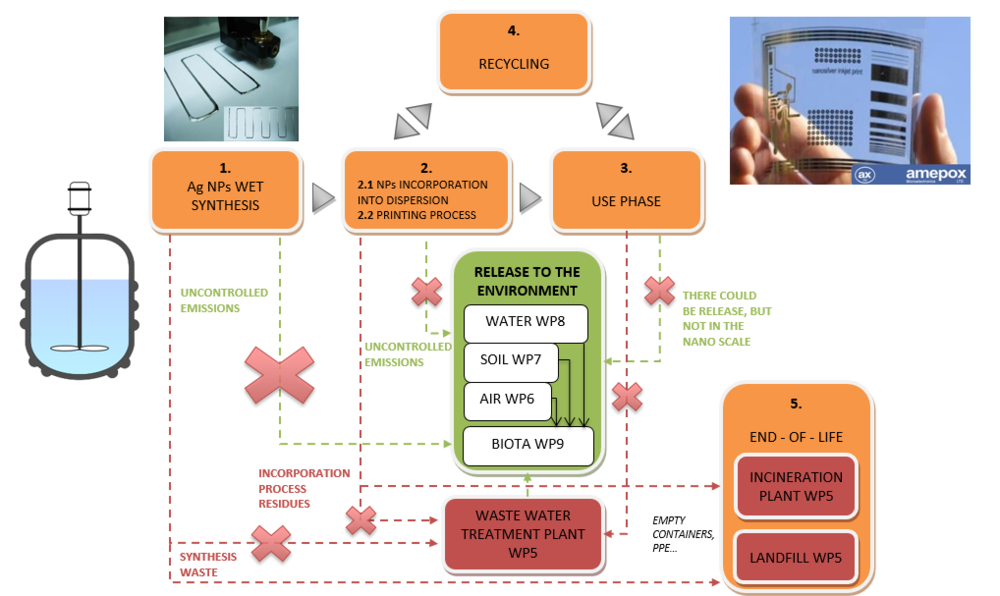
- Synthesis: Some solid waste containing Ag NPs remains from synthesis, but it is immediately reused.
- Printing process: The ink is fused to its support through sintering, during which the nanoparticles aggregate losing their nanoscopic properties. The finished product contains no ENPs.
- Use phase: As no NPs remain, Ag release could take place but not in the nanoscale.
- Recycling: Printed circuits can be recovered and used again for the production of silver precursor.
- End-of-life: Printed circuits are disposed of as electronic material in accordance with national or local law.
Read more |
|
Visit the NanoFASE Library to read summaries: NanoFASE Report D1.2 Report on the pathway analysis |
Contact

Socorro Vázquez-Campos
LEITAT
Email: svazquez@leitat.org
 Andrzej Moscicki
Andrzej Moscicki
Amepox Microelectronics (AXmc)
Email: amepox@amepox.com.pl
