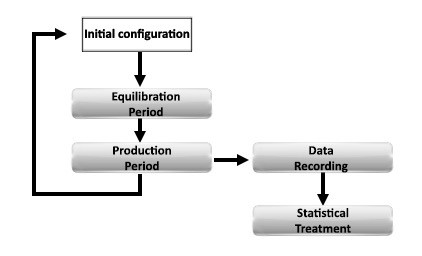
Monte Carlo simulations
The Monte Carlo modeling method uses random numbers to explore configuration space and to derive statistically most favourable conformations or distributions, based for example on the energy variation or values of ENM attachment efficiencies. Monte Carlo simulations represent an important substitute when mathematical analytical solutions are not possible. In our case, upon collision, heteroaggregation between two particles is accepted based on the comparison of the corresponding attachment efficiency with a random number comprised between zero and one.
|
|
Used for |
 Heteroaggregation rate calculation |
Read more |
Read also |
|
NanoFASE Report D8.6 Description of model framework for agglomeration and removal of NMs |
Clavier, A., Praetorius, A., Stoll, S., 2019, Determination of nanoparticle heteroaggregation attachment efficiencies and rates in presence of natural organic matter monomers. Monte Carlo modelling. Science of the Total Environment, v. 650, p. 530-540. Elimelech, M., Gregory, J., Jia, X., 2013. Particle deposition and aggregation: measurement, modelling and simulation. Butterworth-Heinemann. |
Contact
 Serge Stoll
Serge Stoll
Group of Environmental Physico
Chemistry, University of Geneva
Marianne Seijo
Group of Environmental Physico
Chemistry, University of Geneva
