ICP-MS
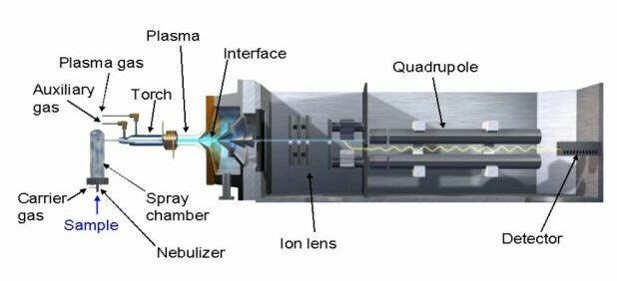
Inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) is one of the most sensitive ways to measure concentrations of elements, usually in aqueous solutions.
ICP-MS is widely used to characterise ENMs, by confirming their elemental composition (including the ratio of core composition and any chemical dopants) and to quantify the presence of ENMs in environmental matrices (soil, organisms, etc.).
Single-particle or spICP-MS is a further advance on the technique, that allows distinction between the particulate form and the dissolved fraction present in the sample, as well as giving particle size information.
 |
|
Used in
Read more |
|
Contact

Geert Cornelis
Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences (SLU)
Email: Geert.cornelis@slu.se